Zetrix Consensus Mechanism: A Blueprint for Security, Scalability, and Decentralisation

Zetrix-BFT (Byzantine Fault Tolerance) Algorithm: Technical Insight
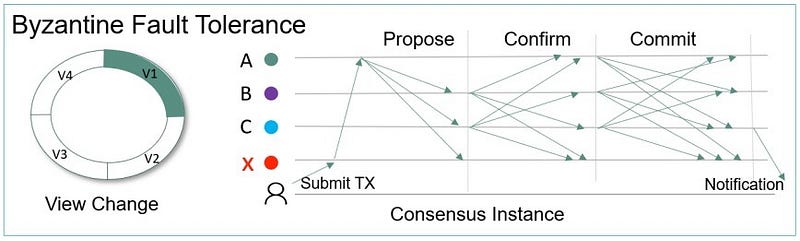
The Zetrix-BFT algorithm is based on the Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) algorithm, ensuring strong consistency and preventing chain forks. This allows for efficient and secure transaction confirmation within seconds. The BFT algorithm is particularly effective in ensuring the integrity of the blockchain by detecting and correcting any potential inconsistencies in the network.
In a distributed system like a blockchain, Byzantine faults can manifest in various ways, with different symptoms observed by different parties. In the context of blockchain networks, where consensus on the state of the ledger is crucial, Byzantine faults often take the form of conflicting information regarding transaction data. This may involve a miner or validator proposing an invalid block or attempting to validate an invalid transaction.
The root cause of such faults can be malicious intent, such as a coordinated attack by node operators, or unintentional issues like faulty hardware or software that inadvertently presents false information. As blockchain networks grow in size, the likelihood of Byzantine faults occurring increases.
The primary purpose of consensus protocols like Zetrix-BFT is not to eliminate Byzantine faults entirely or achieve 100% fault tolerance, but rather to ensure that the system can continue operating despite the inevitable occurrence of such faults. The consensus protocol aims to guarantee that a majority of nodes can reach an agreement while acting in the best interests of the network, allowing the blockchain to maintain the integrity of the transaction ledger.
In summary, the Zetrix-BFT algorithm is designed to ensure strong consistency and prevent chain forks, while also detecting and correcting any potential inconsistencies in the network. By leveraging the Byzantine Fault Tolerance algorithm, Zetrix-BFT provides a robust and secure consensus mechanism that enables efficient and secure transaction confirmation within seconds.
Validating Pool + BFT: Decentralised Participation
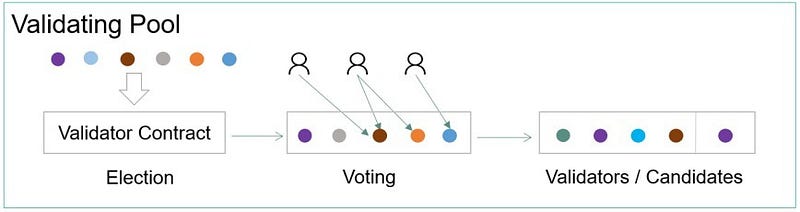
The Validating Pool algorithm enables ordinary users to participate in voting and electing accounting nodes, which generate blocks through the BFT algorithm. This decentralised approach allows for greater user engagement and security. The Validating Pool ensures that the consensus mechanism is robust and resistant to potential attacks by distributing the responsibility of validating transactions across multiple nodes.
Scalable Consensus through Multi-Chain Sharding
Zetrix leverages parallel and diverse multi-chain sharding technology to ensure scalability, addressing the limitations of traditional single-chain architectures. In single-chain systems, performance is constrained by the capacity of individual nodes, causing throughput to eventually hit a ceiling. Additionally, most data is stored on-chain, which fails to meet the performance and capacity needs of various applications.
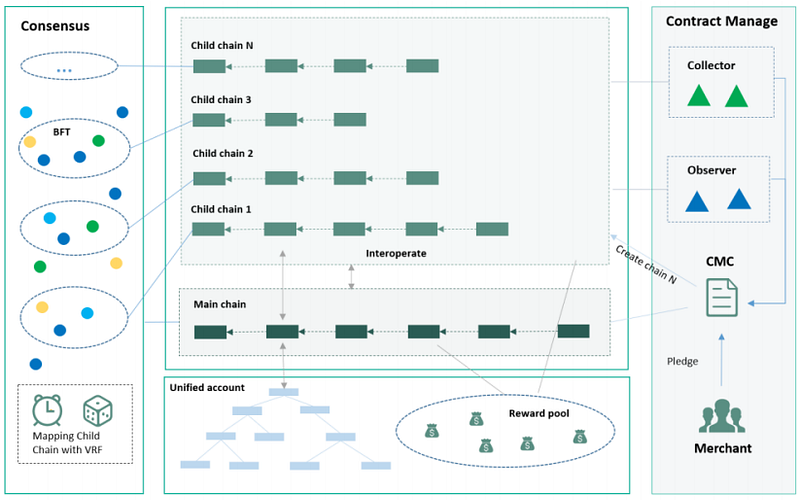
The multi-chain sharding technology overcomes these limitations by splitting data according to different business scenarios, horizontally improving blockchain throughput. This “two-layer capacity expansion technology” allows for the seamless expansion of multiple sub-chains from a main chain. Each sub-chain is responsible for a portion of the calculation and storage tasks, and the number of sub-chains can increase with the volume of business and data.
The main chain manages these sub-chains and ensures overall security, while the sub-chains inherit this security and handle specific business operations. Crucially, the growth of data on sub-chains does not impact the efficiency of the main chain or other sub-chains, effectively achieving resource isolation and maintaining optimal performance across the network.
DPoS Consensus: Incentivising Network Integrity
$ZETRIX token is used in the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, where active staking of $ZETRIX is required to operate validator nodes. This incentivises validators to maintain the integrity of the network and ensures that the consensus mechanism is secure and decentralised. The DPoS consensus mechanism is particularly effective in ensuring that the network is resistant to 51% attacks, as the validators are incentivised to maintain the integrity of the network.
Consensus Node Selection: Ensuring Network Stability
Zetrix allows for the selection of verification nodes to ensure the stability and growth of the network. This ensures that malicious nodes can be excluded from the consensus node group, and high-performance nodes can be elected to join the verification node group. The selection of verification nodes is based on a combination of factors, including the node’s performance, reputation, and stake in the network.
Conclusion
By leveraging these consensus mechanisms, we aims to provide a secure, scalable, and decentralised platform for various blockchain applications, including smart contracts, cross-chain transactions, and asset tokenisation. Our goal is to enable the adoption of blockchain technology at scale while ensuring the integrity and privacy of user data.





